Tungiasis
Tungiasis is an infestation of the skin by a
burrowing flea called Tunga penetrans (also known as
Sarcopsylla penetrans or Pulex penetrans, or
more commonly as the chigoe flea, bicho de pie (bug of the foot),
jigger, nigua, pico, pigue, and sand flea. Chigoe flea is sometimes
confused with chigger or harvest mite.
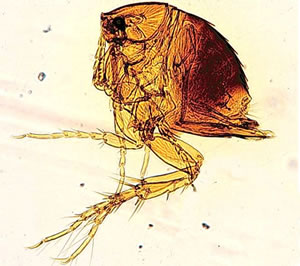
Tunga penetrans (jigger or sand flea).
Life Cycle of the Chigoe Flea
The parasitic chigoe flea lives in warm, dry soil and sand, and
is found commonly in beaches, farms, and wooded areas. Both the
male and female fleas feed on warm-blooded host, but only the
impregnated female flea anchors herself and burrows into the host's
skin. The chigoe flea burrows head first into the upper dermis,
with the tail-end of its abdomen forming an orifice at the skin
surface (often causing white patch with a dark tip, bump or ulceration),
which the flea uses to breathe.
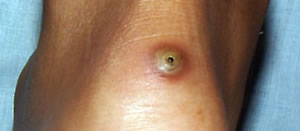
Tungiasis lesion.
In about 1 to 2 weeks, the chigoe flea becomes enlarged (about
the size of a pea) when it becomes full with eggs. It then lays
about 100 eggs through the skin orifice, which fall to the ground.
The flea then dies and is slowly shed by the host. In approximately
3 to 4 days, the eggs then hatch and become adult fleas in 2 to
3 weeks.
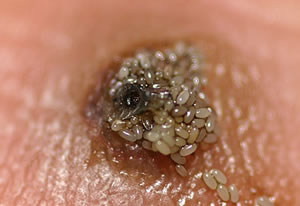
Flea eggs shed from the lesion.
Host of the Chigoe Flea
To reproduce, the chigoe flea requires a warm-blooded host, such
as human, cattle, sheep, horse, pig, rat, and dog.
Symptoms of Tungiasis
The symptoms of chigoe flea infestation include:
- Extreme itching
- Pain
- Inflammation
- Fibrous cyst
- Bumps, lesions or nodules (in form of white or red patches
with dark spots)
- Ulceration, especially in heavy infestation
- Discharge from the ulcer or bump
In heavy infestation, ulceration and fibrosis can occur. Left
untreated, secondary infection such as bacteremia, tetanus and
gas gangrene can occur.
Because the flea has limited jumping ability, the most common
site of infection in human is the feet, especialy in the areas
between the toes and around the toenails.
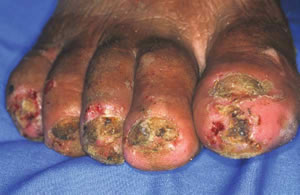
Severe tungiasis of the toes.
Prevalence of Tungiasis
Tungiasis is found mainly in the Africa, especially in Nigeria,
the Caribbean, especially in Trinidad, Central and South America,
and India.
Prevention of Tungiasis
Infection by chigoe flea can be effectively prevented by wearing
shoes and spraying insecticides in affected areas.
Tungiasis Treatment
The treatment options for chigoe flea infestation include:
- Cryotherapy
Similar to cryotherapy for wart, a freezing solution of liquid
nitrogen is applied to "freeze" the tungiasis nodule.
- Topical medicine
Topical anti-parasitic medicine, such as ivermectin (stromectol)
can be used.
- Anti-parasitic drugs
Drugs such as niridazole has been successfully used to kill
embedded fleas in adults and children.
- Petrolatum solution
Another option is to put a thick layer of petrolatum (liquid
paraffin or mineral oil) to suffocate the flea.
- Removal by forcep
When the flea is close enough to the surface, a forcep or a
needle can be used to gently remove it from the skin.
- Surgery
If the flea is engorged with blood, it may be difficult to remove
with a forcep. Here, a minor surgery using a curette to excise
the nodule may be necessary.
After removal of the chigoe flea, topical antibiotics are applied
to the wound. Broad spectrum antibiotics and tetanus shot may
also be given to prevent secondary infections.
Reference:
eMedicine -
Tungiasis


