Impetigo
Impetigo is a contagious bacterial infection
of the skin, characterized by tiny blisters with clear, yellow
fluid discharge.
Symptoms of Impetigo
The symptoms of impetigo include:
- Tiny blisters that rupture easily
- Clear, yellow fluid discharge from the rupture
- Yellow-colored crust from the dried discharge
- Scabs
- Itching or burning sensation
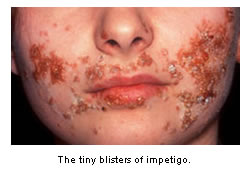
Impetigo blisters occur most commonly on the face, scalp, arms
and legs, especially near cuts, scratches, or insect bites on
the skin.
Impetigo is very contagious and can be easily spread to other
parts of the body or another person by direct contact or shared
clothings or towels.
To avoid scarring, blisters should not be scratched or picked.
Who Gets It?
This condition affects mostly young children, although it may
also occur in adults. Adult impetigo cases are usually accompanied
by other skin disorders, such as eczema.
Prevention of Impetigo
To prevent the transmission of impetigo, do the following:
- Avoid direct skin to skin contact with infected person
- Do not share towels, washclothes, or clothing with an infected
person
- Wash your hands often with antimicrobial soap
- Gently wash blisters with antimicrobial soap several times
a day
Treatments of Impetigo?
Your doctor may prescribe:
- Oral antibiotics
Usually a 10-day course of penicillin, cephalexin, or erythromycin.
- Topical antibiotics, such as mupirocin.


