Cellulitis
Cellulitis is a very serious bacterial infection
of the skin and underlying fat tissue.
This condition is not to be confused with cellulite,
a cosmetic condition where unattractive lumps of fat is observed
in the thighs, stomach, and buttock areas.
Symptoms of Cellulitis
The symptoms of cellulitis include:
- Red, swollen skin
- Warm or hot area in the skin
- Pain and tenderness
- Orange-peel look of the skin
- Fever and chills
- May or may not be accompanied by headaches
Cellulitis is often accompanied by other disorders, such as chickenpox,
varicose veins, leg ulcers, and chronic venous insufficiency.
It can also occur after skin injury or during healing of a surgical
wound.
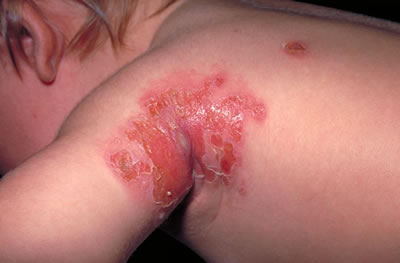
Cellulitis in a child due to infection at vaccination site.
Left untreated, the infection can spread to the bloodstream in
a life-threatening condition called septicemia.
In rare cases, secondary infections such as fasciitis
can develop. In fasciitis, infection by "flesh eating bacteria"
can cause rapid destruction of skin, fat, and connective tissue.
In this case, surgery to cut away infected tissue is the only
option.
Who Gets Cellulitis?
Although it can occur in anyone, the following people are more
susceptible to cellulitis:
- Those with venous conditions, such as varicose vein, venous
insufficiency
- Those with leg ulcers
- Those with prior episodes of cellulitis
- Those who have healing surgical wounds
Prevention of Cellulitis
To prevent bacteria from entering openings in the skin, wash
all wounds, scraps, cuts, and insect bites with antibacterial
soap.
When Should I See a Doctor About Cellulitis?
Immediately - cellulitis need to be treated as early as possible.
If not, it can develop into serious, life-threatening conditions.
Treatment of Cellulitis
When caught early, your doctor may prescribe oral antibiotics.
For more advanced cases, or if oral antibiotics do not work,
then a hospital stay is required. An intravenous antibiotic treatment
is administered.


