Ringworm (Tinea corporis)
Ringworm or tinea corporis
is not a worm - actually, it is a fungal infection of the skin.
Symptoms of Ringworm
The symptoms of ringworm include:
- Red, ring-shaped patches
- Slightly elevated bumps with scaly border
- Itching and pain
- Hair loss, redness, and flaking skin (when on the scalp)
Ringworm can affect all parts of the body - however, it is most
commonly found on the scalp (called tinea capitis), chest, back,
arms, and legs.
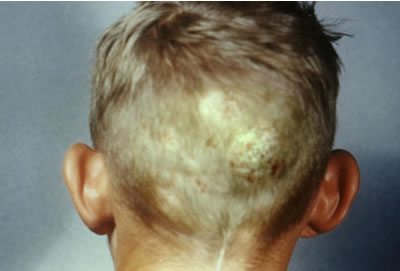
Ringworm infection of the scalp or tinea
capitis.
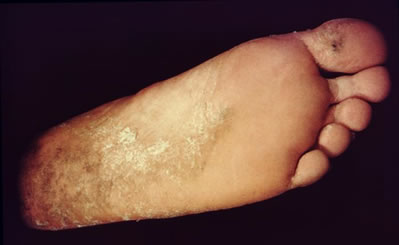
Ringworm infection of the foot or tinea
pedis.
Causes of Ringworm
Several species of the Microsporum and Trichophyton
fungi. These fungi are very contagious, and are transmitted by
direct contact or shared items, such as clothings, combs, brushes,
hats, and towels. It is thought that even pets can transmit this
disease!
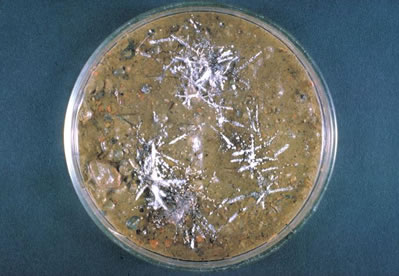
Trichophyton terrestre in a culture
dish.
Who Gets Ringworm?
Mostly children - however, it may develop in men and women of
all ages.
Ringworm Treatment
Ringworm treatments include:
- Over-the-counter antifungal creams containing clotrimazole
or miconazole
- Using shampoo with selenium sulfide to reduce shedding of
the fungus
- Prescription antifungal creams
- Oral antifungal medications
Over-the-counter creams are usually effective against ringworm
infection on the skin. Infection on the scalp, however, require
prescribed oral medication. Left untreated, ringworm on the scalp
can cause permanent hair loss and scarring.


