Raynaud's Disease / Phenomenon
Raynaud's Disease is actually not a disease
of the skin - it is caused by blood circulation problem. In this
condition, the skin color in the tips of the fingers and toes
change color when exposed to changes in temperature.
This condition is named after Maurice Raynaud (1834-1881), a
French physician who first desribed its symptoms.
How do I Pronounce it?
RAY-noz.
Raynaud's Disease Symptoms
The symptoms of Raynaud's Disease are:
- Color change in the fingers, toes, and earlobes when exposed
to cold or stress
- When warmed, the skin color turns back to normal
- Burning, tingling and pin-and-needles sensation during color
change
In rare, severe cases, gangrene can develop at the tip of the
fingers.
Causes of Raynaud's Disease
The change in skin color is caused by the constriction or narrowing,
or spasm of blood vessels in the finger, toes, and earlobes. This
causes blood flow to the area be reduced, and the skin color to
turn white (pallor).
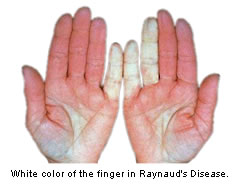
When the oxygen supply to the area is depleted, the skin color
turn blue (cyanosis). When blood returns to the area, the skin
color turn red (rubor).
Classic Raynaud's Disease include all 3 color changes. However,
they do not always occur in all people or in all flare-ups of
the condition.
Who Gets It?
Raynaud's Disease occurs most often in young women between 18
and 30 years of age, and may be accompanied by other illnesses
such as arthritis, scleroderma and lupus.
When it occurs only by itself, it is called Raynaud's Disease
or Primary Raynaud's. When accompanied by other disease,
it is called Raynaud's Phenomenon or Secondary Raynaud's.
Prevention of Raynaud's Disease
If you have Raynaud's Disease, you can prevent its occurrence
by:
- Keeping warm by wearing warm clothes, gloves, and socks
- Avoiding touching cold or frozen objects, or using gloves
- Avoiding stress
- Avoiding smoking
- Avoiding taking decongestants or diet pills that contain phenylpropanolamine
Treatment of Raynaud's Disease
Raynaud's Disease treatment include:
- Prescription medicine
You doctor may prescribe medicine that dilate or enlarge blood
vessels, such as the calcium channel blockers nifedipine and
diltiazem.
- Biofeedback training
This technique is used to gain control over skin temperature,
heart rate, blood pressure, and other involuntary body functions.
- Surgery
In rare cases, a surgery called sympathectomy, where nerves
that affect the blood vessels and cause them to constrict in
the fingers are cut. This procedure is not necessary in most
cases, and have varied level of success.


