Scabies
Scabies is an allergic response caused by an
infestation of a small mite (Sarcoptes scabiei
var. hominis) that burrows in the skin.
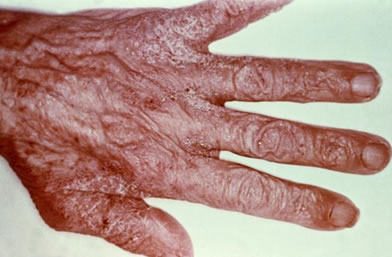
Rash due to infection by Sarcoptes
mite.
Symptoms of Scabies
The symptoms of scabies are:
- Small, red bumps
- Severe itching, which intensify at night
- Scaling, crusting, and redness of the skin caused by the scratching
- Burrows or lines that are slightly raised and about 1/8th
inch in length, sometimes with black speck at one end
- Burrows are often seen in the inner wrist and between the
fingers (in the finger web)
Scabies often affect the following area:
- Finger web
- Wrist
- Underarm
- Genital area, such as scrotum and penis
- Breast
- Elbows
- Buttocks
Sometimes a secondary bacterial infection develop at the site
of the scabies infection, especially if the skin is broken through
by scratching.
An animal with scabies ticks or mange can cause scabies infection
in human. However, this form is usually mild and the mites die
within a couple of days without laying eggs.
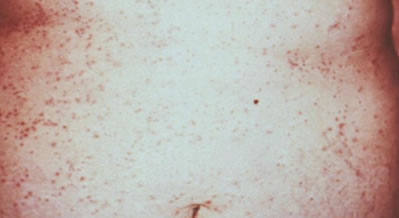
Abdominal rash in a woman infected with
canine scabies.
Cause of Scabies
A mite called Sarcoptes scabiei. This mite lays eggs
under the top layer of the skin, which hatches about 7 to 10 days
later. These mites caused an allergic reaction.
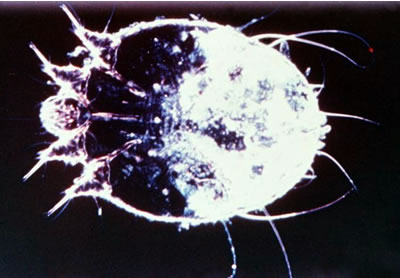
Sarcoptes scabiei or itch mite.
Is it Contagious?
Yes, scabies is highly contagious. It can be transmitted from
people to people by:
- Direct contact
- Through shared clothings and towels
- Pets that are infected by scabies
Treatment of Scabies
Scabies treatment include:
- Permethrin cream
- Lindane lotion
- Oral sedating antihistamine to relieve itching
The topical cream and lotion should be used not only by the person
who is affected, but also his or her entire household members.
Mite eggs can persist in clothings and bedsheets, therefore they
should be laundered and dried in a dryer under the hot setting
daily. If this is not possible, then the infected clothings should
be sealed inside a plastic bag for at least 10 days to kill the
mites.


