Eczema (Atopic Eczema)
Atopic eczema or atopic dermatitis
is a common skin condition characterized by itchy rashes and inflammation.
Symptoms of Eczema
The symptoms of atopic eczema include:
- Red rashes
- Dry, flaky, and irritated skin
- Itching
- Inflammation
- Bleeding and crusting of the skin (occassionally caused by
scratching)
The rashes tend to occur on the fold of the skin on the elbow,
back of the knees, front of the ankles and back of the neck.
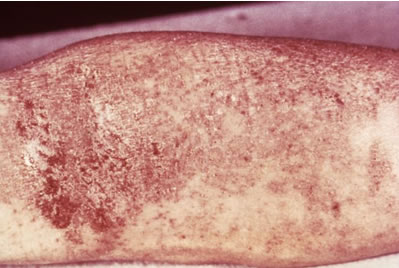
Skin rash & inflammation due to eczema.
Causes of Atopic Eczema?
The exact cause of atopic eczema is not known, but is thought
to be related to allergic reactions. Indeed, "atopic"
refers to the presence of a circulating antibody called atopic
reagin in the blood.
Who Gets It?
Atopic eczema is an inherited condition and particularly tends
to run in families with a history of asthma or hay fever. This
condition usually develops in infancy or early childhood.
This condition usually improves with age, however recurrence
may happen at any age and may be worsen by secondary bacterial
infection at the site of the rash.
Prevention of Atopic Eczema
The following can help prevent the recurrence of atopic eczema:
- Do not wear wool or rough clothings that can irritate the
skin
- Do not wear clothings that are too tight or too warm
- Wear light cotton clothings
- Shower with warm water and antibacterial soaps
- Use moisturizers to prevent dry skin
- Avoid scratching an itch, as this may worsen eczema
If you have eczema, even if the condition is not currently active,
you should avoid getting vaccinated for smallpox in order to avoid
a potentially serious condition called eczema vaccinatum.
Treatment for Atopic Eczema
Treatments for atopic eczema are:
- Corticosteroid creams and ointments to reduce inflammation
- Oral sedating antihistamines to induce sleep and avoid nighttime
itching
- Ultraviolet light therapy
- Antibiotics, if secondary bacterial infection occurs


