Hives or Wheals (Urticaria)
Hives, also called wheals and
urticaria, are swollen red patches on the skin.
They are caused by a histamine reaction, and are usually accompanied
by itching, and sometimes by a burning sensation, flushing and
wheezing.
Symptoms of Hives
The symptoms of hives are:
- Multiple patches in circular, semicircular or ring shape
- Raised, swollen bumps
- Pink, red, or white in color with the central area paler than
the outer portions
- About 1 inch to more than several inches in diameter
- Severe itching
- Burning or stinging sensation (occassionally)
- Flushing or wheezing (occassionally)
These patches can occur at any part of the body, and usually
disappear after 1 hour. New spots may come and go for hours or
even weeks. In rare cases of chronic hives, these patches are
present daily for many years.
The wheezing associated with hives is caused by swelling of the
airways, similar to the swelling of the skin. If this swelling
blocks the airways completely, hives can be life-threatening and
therefore require immediate medical attention.
Causes of Hives
Hives are caused when histamines are released
by the body. This release of histamine is triggered by:
- Medications
- Food, such as chocolate, nuts, shellfish, cheese, berries,
and tomatoes
- Insect bites and contact with caterpillar spines
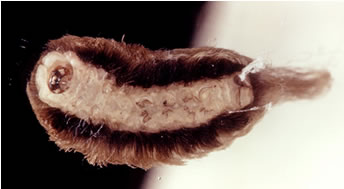
Skin contact with the hair-like spines of
Megalopyge opercularis or
hive-producing caterpillar can induce hive breakout.
- Infections
- Stress
- Exercise
- Exposure to sunlight
- Exposure to cold
Treatment of Hives
Hives treatments include:
- Prescription and over-the-counter non-drowsy antihistamines
for the daytime, such as cetrizine and loratadine.
- Over-the-counter, sedating antihistamines before bedtime,
such as diphenhydramine and chlorpheniramine
- Cool compresses to the affected areas
- Epinephrine or adrenaline injection, intravenous antihistamine,
and corticosteroid medicines for hives patients with difficulty
in breathing.


